Digitalization and blockchain are changing the face of multiple industries, and healthcare is also one of them. Blockchain is facilitating the healthcare industry by improving data security, simplifying the process of managing patient records, and speeding up clinical research.
It is already being used to track pharmaceuticals and to manage genomic data that is applied to support more personalized medical care.
Blockchain has been used in the healthcare industry in all aspects, such as the safety of patient information and optimization of the pharmaceutical supply chain.
What is Blockchain in a Nutshell?
Blockchain is essentially a shared, distributed and secure digital ledger. Each block stores data or transactions and once they are added, the information cannot be changed without a trace. Each of the nodes (or computers) of the system possesses a full copy of the chain and helps to verify the new data before it is registered.
In healthcare, these blocks could include data such as patient records, prescriptions, or insurance claims. Blockchain is decentralized, transparent, and secure; thus, it works differently than the traditional systems in which the data is in the hands of one entity, be it a hospital or an insurer.
Potential of Blockchain in Healthcare
Safe Health Information Exchanges
Blockchain establishes a secure system where approved doctors can access patient records immediately.
All the updates would be written irreversibly, forming an audit trail.
HIPAA rules stay in place, and smart contracts make sure only the right ones get access.
The patients would determine access to their information by using the private keys.
Processing and Payments
Insurance claims would be automatically processed and verified using smart contracts.
No delays in payments with certain rules and regulations.
Less paperwork would mean reduced cost of administration.
Patients and providers can monitor the status of claims in real-time.
Drug Supply Chains and Clinical Trials
Blockchain protects the results of clinical trials through time-stamping entries.
Smart contracts automatically enforce research protocols.
Monitoring of the supply chain of medications is helpful in avoiding counterfeit drugs, thanks to technology.
It can also make it easier to get the consent of the patient and handle the same.
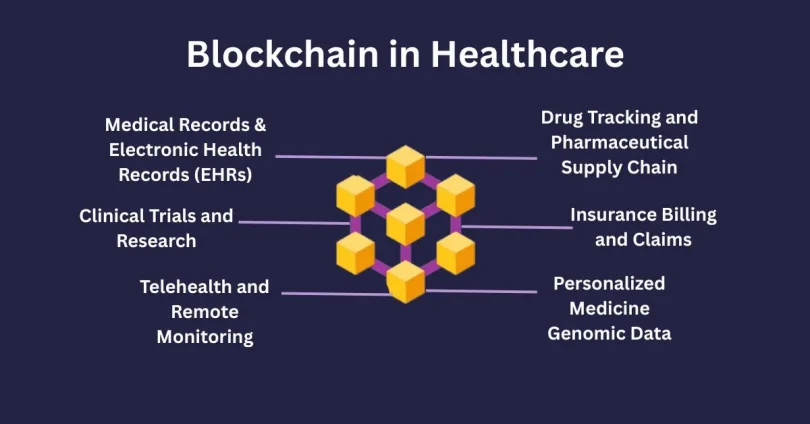
Significant Uses of Blockchain in Healthcare
1. Medical Records & Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
Records are incomplete, exposed and isolated.
Blockchain can provide secure, shared access, and patient control, and tamper-proof storage.
This results in greater precision with faster and seamless results.
2. Drug Tracking and Pharmaceutical Supply Chain
The issue: Fake medicines are estimated to be about 10 percent of the total world medicines.
Blockchain gives an advantage to track each unit of drugs during the manufacturing process to delivery. This will reduce the fake medicine and protect the health of consumers.
IBM-Merck-supported projects, MediLedger, Blockpharma, and FarmaTrust are a few example of organizations that are using this technology to track their medicines.
3. Clinical Trials and Research
The trial data can be altered or destroyed, and the consent tracking is unclear; it is a big problem for healthcare providers. With blockchain behind it, every consent action gets tracked, and the info sticks around for good, no edits, no erasing.
4. Insurance Billing and Claims
Manual work takes a lot of time, wears you out, and often leads to mistakes, it’s slow and draining. Blockchain provides an efficient solution against manual claims and billing; its smart contracts automate and verify payments, minimizing fraud and paperwork.
5. Telehealth and Remote Monitoring
IoT and telehealth are growing at a high rate. In my experience, it’s already catching on and is only going to get bigger soon.
The ways blockchain can help:
- Stores device data logs securely
- Manages consent
- Sends automatic notifications using smart contracts.
6. Personalized Medicine Genomic Data
Why it is important: Genetic information is cumbersome and confidential.
Blockchain role: Stores and shares genomic data safely and allows privacy-controlled access to tokenized research.
Real World Applications of Blockchain Already in Industry
Safe Health Information Exchanges (HIEs)
Pilot projects already use blockchain-based HIEs that enable authorized healthcare providers to access patient-approved records in real-time.
Clinical Trial
Blockchain will add time stamps to every entry that is involved in trials, which will help in the accuracy of the data and proper documentation of consent.
Pharmaceutical Supply Tracking
Blockchain enables drug manufacturers and distributors to trace the batches of medication produced to the shelves of the pharmacies, which means that the products are genuine.
Smart Billing
Blockchain-based billing platforms allow the detection of duplicates and automate insurance reimbursements.
Challenges and limitations
High Upfront Costs: The creation of blockchain systems is an infrastructure, integration, and talent-intensive investment.
Regulatory Obstacles: The necessity to maintain an immutable record on blockchain should be reconciled with the privacy regulations like GDPR and HIPAA that require data deletion functionality.
Slow Adoption by Industry: Lack of technical skills and procedures has made the majority of healthcare providers hesitant to adopt blockchain solutions.
Ongoing Technical Problems: Scalability issues, high energy consumption, and the impracticality of ensuring a proper connection between physical assets and digital blockchain records are still to be addressed.
Bottom Line
Blockchain has stopped being a hype; it is already transforming the healthcare industry by enhancing the safety of data, standardizing patient records, accelerating clinical trials, tracking drugs, and guarding genomic data. Of course, there are challenges in the way in the form of the costs, the regulation, and the complexity of the technology. Whether it is possible to be a leader in the healthcare industry, develop the technology, or contribute to the policy making, this is the time to think about blockchain pilot programs, join industry consortiums, and cooperate with the existing vendors. Start off small; start with a pharmacy traceability or an EHR sharing programm and expand that way.
In the future healthcare system with a secure environment and transparency as well as patient-centered will become a reality, and it starts today.
FAQs
Blockchain acts as a decentralized, tamper-proof ledger across multiple computers. In healthcare, it securely records patient data, prescriptions, insurance interactions, and drug shipments, all accessible to permitted users.
By giving patients control over their data and enabling multiple providers to view updated information, blockchain resolves fragmentation issues. It ensures records are accurate, auditable, and easily shared across authorized systems.
Absolutely. It enables full traceability of drug batches from manufacturer to pharmacy. Immutable tracking significantly reduces counterfeit risk. According to the WHO, about 10% of global medicines are fake.
Key challenges/barriers include:
Costs: Infrastructure and expertise are expensive
Regulations: Immutability and data-deletion laws like GDPR/HIPAA must align
Adoption: Lack of standards and technical know-how slows its uptake.
Technical issues: Scalability, energy usage, and linking physical assets are still under development.


Leave a Comment