In this world of information where data is the power. However, handling large volumes of data is not straightforward; it can be disorderly and challenging.
Imagine a DBMS as a conductor of a large orchestra, who is responsible for the coordination and the smooth functioning of a symphony of data. It serves as a main repository for data storage, retrieval and operation all in a secure, error-free, and accessible manner.
So, let’s take a closer look at what a DBMS does. Furthermore, why is this a vital tool? This article will help you understand the core functions, the advantages and disadvantages of DBMS, and help you realize the power that data can have on your work.
Thus, whether you’re an entrepreneur, developer, or just a curious person, all you need do is keep reading and find out how Database Management Systems are integral to the success of our data.
Guide to Database Management system
What is Database Management system (DBMS)
Database Management Systems (DBMS) is a name that is used to refer to a class of software products that provide means for the storage, retrieval and execution of queries on data.
The role of the DBMS is to provide a common point between end-users and databases, where data can be created, read, updated and deleted within the database.
The functions/Goals of DBMS:
The DBMS supervises the database engine and the database schema, thereby enabling users or other programs to manipulate data or extract from it.
It provides a guarantee for data security, integrity, concurrency, and unified administrative processes.
Lastly, DBMS optimizes data structuring by using normalization, a diagramming technique that breaks up large tables into smaller ones to eliminate the redundancy of attribute values. While traditional file systems are superior in terms of flexibility and file backup, DBMS offers enhanced flexibility and an advanced backup system.
Why is DBMS Used?
DBMS is the tool used for the organization of database files and provision of end-users with more control and access to their data. It also calls for making users able to perform data manipulation operations on their files’ databases, such as creating, editing and updating.
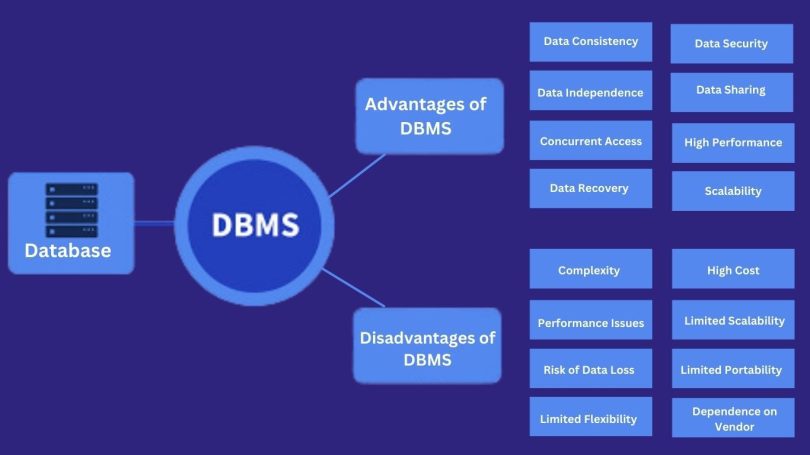
Advantages of DBMS:
DBMS provides numerous benefits or advantages or pros compared to traditional file-based systems…
- Data Consistency: It guarantees data consistency through rules and constraint enforcement, resulting in high accuracy and confidence in the data.
- Data Independence: DBMS makes changes to the database schema possible without affecting the application programs, thus making maintenance and update easier.
- Concurrent Access: Allows multiple users to simultaneously access the database in a transaction that prevents conflicts and improves efficiency in data manipulation.
- Data Security: DBMS features include controls to protect access to the data, thus preventing unauthorized data access and data security.
- Data Recovery: DBMS implements a recovery mechanism in case of failure and backup creation for disaster recovery which increases the reliability of data.
- Data Sharing: DBMS allows the access of the data by multiple applications at a time, thereby improving the data consistency and eliminating redundancy.
- High Performance: It uses different techniques such as indexing, caching and partitioning in order to improve retrieval performance.
- Scalability: This (DBMS) can also deal with big data and support the growing number of users and transactions, providing optimal scalability.
- Data Validation: DBMS enforces data integrity rules when user-entered data is validated against the constraints already defined.
- Data Abstraction: Separates users from the physical storage, which makes data management and manipulation more convenient.
- Data Representation: Stores data in a logical and orderly fashion, allowing fast retrieval, searching and manipulation of data.
Disadvantages of DBMS:
Although Database Management Systems offer numerous “advantages”, they also possess certain “disadvantages” that necessitate consideration when choosing a system for “data storage” and “management”.
- Complexity: DBMSs can be complicated especially for large and complex databases, which need expertise and resources for good management.
- High Cost: While initial acquisition of DBMSs may be expensive and ongoing maintenance and support may be costly, organizations may find financing these aspects a challenge.
- Performance Issues: DBMSs, which are inadequately designed, indexed or optimized, can experience performance issues like slow data retrieval, and this affects operational efficiency.
- Limited Scalability: Some DBMSs are less scalable, especially when working with the largest and most complex databases, resulting in growth and expansion problems.
- Hardware and Software Requirements: The deployment of DBMSs requires configuring hardware and software particularly, which may incur additional costs and resource allocation to organizations for meeting these requirements.
- Risk of Data Loss: DBMSs may face data loss or corruption if not exceptionally backed up and maintained, which will render them untrustable in terms of integrity and availability of critical data.
- Limited Portability: Certain DBMSs can lack portability across different platforms or operating systems, which results in a very low level of flexibility and interoperability in heterogeneous environments.
- Limited Flexibility: Some DBMSs may have reduced flexibility and cannot accommodate certain types of data or queries, thereby constraining the usefulness of applications they can efficiently support.
- Limited Query Capabilities: DBMSs might not be able to handle the complex queries or the specific types of data analysis, hence limiting the system’s analytical capabilities.
- Dependence on Vendor: It can be dependent on vendor support and updates which is a risk for the system as companies can change their policies, discontinue their products or change significantly.
The choice of DBMS should be made after analyzing the advantages and disadvantages of the different types of DBMS systems.
Thorough consideration and balancing of such factors against the organization’s particular needs and demands are essential for the effective selection of DBMS for the organization.
DBMS Components and Features
The DBMS encompasses various components and features essential for efficient database management…
Data Storage:
Among the duties of the file system is the physical storage and retrieval of data from the disk storage, such as the definition of the logical schema, allocation of storage space, and communication with the operating system to read and write data blocks.
Data Security:
Secures data confidentiality and disallows unauthorized access through user account management, access control mechanisms, auditing of user activities, encrypting sensitive data and masking data.
Multiuser Access Control:
Manages the concurrent access from the users and processes to maintain data integrity using concurrency control, isolation levels, atomicity, durability, and consistency.
Backup and Recovery:
Provides utilities to perform regular backups and restore of data and metadata, including online/offline backup, point-in-time recovery, log-based recovery archiving and mirroring/replication capabilities.
Data Integrity:
Validates data to meet the integrity constraints such as entity integrity, referential integrity, domain integrity and custom constraints, thus ensuring accuracy of the data stored.
Transaction Support:
This offers an opportunity to perform a group of operations in a single transaction, hence providing for the transaction initiation, isolation, recovery, locking, and logging for auditing and crash recovery purposes.
Crash Recovery:
Ensures the database to be recovered in a manner that is reliable after unplanned failures or crashes, using methods like write-ahead transaction log, undoing of uncommitted changes, restoration of corrupted data files, releasing of locks as well as restarting of transactions.
Conclusion:
With this knowledge about Databases Management Systems, I hope that you will see the importance of this in handling the increasing amount of information. Whether you’re a business owner striving to improve operations, a developer constructing data-driven applications, or a mere person who likes to know the unknown forces that drive our information age, understanding DBMS is useful. Not only that, it gives you the ability to unlock your data’s potential and turn it into chaos of information into a harmony of insights and possibilities. Go deeper and see the different types of DBMSs, query languages and build your own data system. In the end, rehearsing the consonance of data may be challenging, but the reward is unlimited. Thus, here is the starting point, grab that electric baton, and compose a musical success with the help of DBMS!

Leave a Comment